Smart City
Cities traditionally developed organically with sole purpose on elevating living standards via economic means. Smart cities are loosely defined as cities with emphasis on creating a viable and environmentally friendly communities with excellent economic prospects.
Urban planning focus of Smart Cities are not limited to addressing environmental concerns. Advanced Information and Communication Technology (ICT) processes are integrated to complement infrastructure and enhance its social capital. Communities benefit from city-wide integration of technology and increase the city's overall competitiveness. High speed internet network is an important criteria for Smart City implementation.
Smart Cities focuses on five key aspects of urban living. The city is designed to coexist with nature while minimising our footprint. Residents have access to affordable housing, quality education, healthcare and maintain optimum work life balance. There is a strong sense of community fostered through public participation in local policies and activities. The sustainability agenda encourages innovation in Green Technology and efficient resource management framework. Renewable energy sources and advanced green building technology should be utilised.
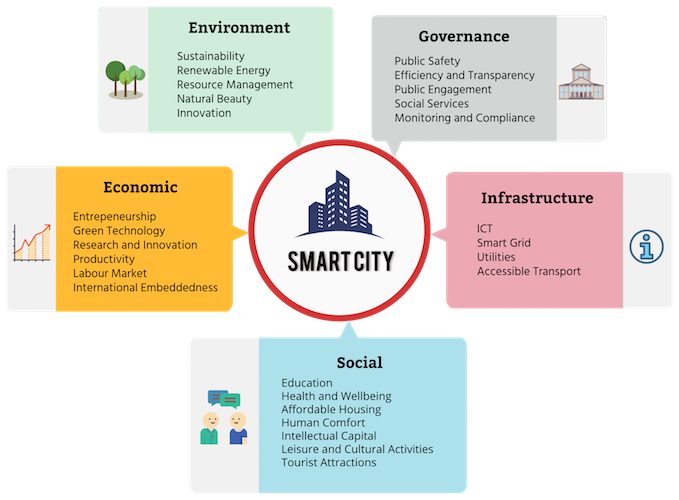
Environment
- Sustainability
- Renewable Energy
- Resource Management
- Natural Beauty
- Minimising Pollution
- Research and Innovation in Green Technology
Economic
- Entrepreneurship
- Green Technology
- Research and Innovation
- Productivity
- Labour Market
- International Embeddedness
Governance
- Public Safety
- Efficiency and Transparency
- Public Engagement
- Social Services
- Monitoring and Compliance
Social
- Education
- Health and Wellbeing
- Affordable Housing
- Human Comfort
- Public Participation
- Intellectual Capital
- Leisure and Cultural Activities
- Tourist Attractions
Infrastructure
- ICT
- Smart Grid
- Utilities
- Accessible Transport
Smart Grid and ICT
Smart Grid is a global initiative to increase use of information and communication technology (ICT) in power generation, power delivery systems to provide real time monitoring and control. Real time monitoring is useful for holistic resource management strategies and reduces system outages. An ideal Smart Grid system will display the following characteristics :
- Self healing
- High reliability and high power quality
- Resistant to cyber attacks
- Accommodates a wide variety of distributed generation and storage options
- Optimises asset utilisation
- Minimises operations and maintenance expenses
ICT usage is not limited to power delivery systems. Other operations can benefit from city-wide ICT integration, including traffic management, advanced building management systems, education systems and security systems. A Central Distributed Load Dispatch Centre will act as the central hub to oversee the ICT applications. This allows authorities and utility operators to monitor load demand, traffic conditions, fire hazards and other information in real time. Next generation wireless sensor network and high speed internet connection will form the backbone for information exchange. Implementation of ICT services require robust, secure data centres and servers to minimise disruptions.
